Table of contents
Introduction to Bitcoin
Where do new bitcoins come from?
How to start using Bitcoin
Bitcoin halving
Common Misconceptions About Bitcoin
Bitcoin scalability
Participation in the Bitcoin network
Chapter 1 - Introduction to Bitcoin
Content
What is Bitcoin?
Why use Bitcoin?
What makes Bitcoin valuable?
How does Bitcoin work?
What is blockchain?
Is Bitcoin legal?
Bitcoin history
Who created Bitcoin?
Is Satoshi the pioneer of blockchain technology?
Digital currency before Bitcoin
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a digital form of money, but unlike the conventional fiat currencies we are all so accustomed to, it is not under the control of a central bank. Instead, the basis for running the Bitcoin financial system is thousands of computers distributed throughout the world. Anyone can participate in this ecosystem after installing certain open source software.
Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency to be announced in 2008 (and launched in 2009). It provides users with the ability to send and receive digital money (bitcoin, lowercase b, or BTC). But the main quality that makes this currency so attractive is that it cannot be censored, funds cannot be spent more than once, and transactions can be made at any time and from anywhere.
Why use Bitcoin?
People use Bitcoin for a number of reasons. Many people value the first cryptocurrency for its inclusive nature (from the English permissionless), i.e. Anyone with an internet connection can send and receive these coins. It is somewhat similar to cash in that no one can stop you from using it, and this digital advantage means that with Bitcoin you can exchange currencies around the world.
What makes Bitcoin valuable?
Bitcoin is decentralized, censorship-resistant, secure and borderless.
This latter quality has made it extremely attractive for use cases such as international money transfers and payments (remittances), provided the user does not want to disclose their personal data (as is the case with a debit or credit card).
Instead of spending their bitcoins, many people choose to hold them for the long term (also known as hodling). Bitcoin has earned the nickname “digital gold” due to the limited number of coins available. Some investors view Bitcoin as a store of value. The reason for this was the presence of factors such as scarcity and difficulty of production, it is also often compared to precious metals such as gold or silver.
Holders believe that the presence of these qualities, coupled with global availability and high liquidity, make it an ideal vehicle for preserving wealth over long periods. They believe that the value of Bitcoin only continues to increase over time.
How does Bitcoin work?
When Alice creates a transaction for Bob, she doesn't send the funds the way you expect. This has nothing to do with the digital equivalent of handing him a dollar bill. It's more like Alice writing on a piece of paper (which is available for everyone to see) that she is giving Bob her dollar. When Bob sends the same funds to Carol, she can see that Bob has money by looking at the transactions recorded on the worksheet.
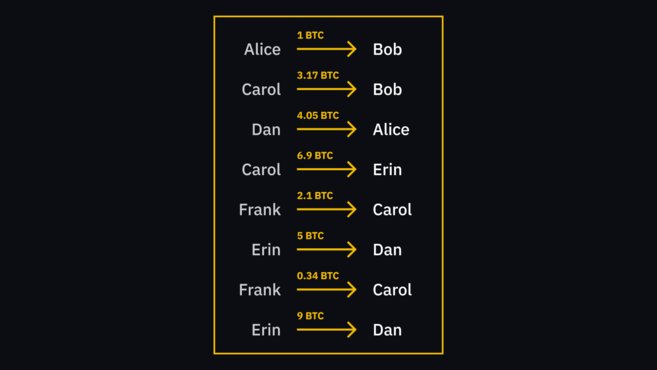
This sheet represents a special type of database and its name in the Bitcoin system is blockchain. All network participants have copies of such a database, which are stored on their devices, and they are constantly in contact with each other to synchronize new information.
When a user makes a payment, they broadcast it directly to a peer-to-peer network, which is not a centralized bank or remittance processing institution. To add new information, the Bitcoin blockchain uses a special mechanism called mining. It is through this process that new blocks of transactions are recorded as records in the blockchain.
What is blockchain?
A blockchain is a ledger or general ledger that is designed solely for adding information. Once data has been recorded in such a book, it is almost impossible to change or delete it. Blockchain achieves this by having a pointer to the previous block in each subsequent block.
This pointer is the so-called hash of the previous block. Hashing involves passing information through a one-way function to obtain a unique fingerprint of the input data. If the input data is subject to even the smallest changes, its imprint will become completely different. Since the length of the chain of interconnected blocks is constantly increasing, users do not have the opportunity to change the old entry, due to the fact that this would require recognizing the invalid status of all subsequent blocks. This structure is one of the main components that ensures the security of the blockchain network.
We recommend that you read our introduction to blockchain systems. See article: “Blockchain technologies. A Beginner's Guide."
Is Bitcoin legal?
Bitcoin is completely legal in most countries in the world. However, there are a few exceptions, due to which you will definitely need to familiarize yourself with the jurisdiction of your state regarding digital currencies before investing in it.
In countries where this type of money is enshrined at the legislative level, government authorities apply various regulatory approaches to it in the form of taxation and rules of use. The regulatory framework as a whole is still underdeveloped and is likely to change in the coming years.
Bitcoin history
Who created Bitcoin?
Nobody knows the creator of the first cryptocurrency! The person who developed Bitcoin used the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto, but exact information about this person is completely missing. Satoshi can be one person or a group of developers anywhere in the world. The name is of Japanese origin, but the level of English proficiency has led many to believe that he, she or they are from an English-speaking country.
It was Satoshi who published the Bitcoin whitepaper and its software, but then he disappeared in 2010.
Is Satoshi the pioneer of blockchain technology?
By the time of its appearance, Bitcoin combined a number of technologies that were already existing. The concept of a block chain did not appear with Bitcoin. The origins of this immutable data structure can be traced back to the early 1990s, when Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta proposed a system for creating timestamps for digital documents. Similar to today's blockchains, they used cryptographic methods to protect data and prevent the possibility of falsifying information.
Interesting fact: Satoshi’s whitepaper does not use the term “blockchain”.
See also: "History of Blockchain".
Digital currency before Bitcoin
Bitcoin was not the first of its kind, but it is the most successful attempt at digital cash. However, previous attempts provided Satoshi with the opportunity to invent such a system:
DigiCash
DigiCash is a company founded by cryptographer and computer scientist David Chaum in the late 1980s. It was presented as a privacy-focused solution for online transactions based on an article authored by Chaum himself (details at the link).
The DigiCash model was a centralized system, but nevertheless, it was quite an interesting experiment. The company later went bankrupt, which Chaum believes was because they started before e-commerce really took off.
B-money
The B-money system was originally described in a proposal published in the 1990s by computer engineer Wei Dai. He was quoted in the Bitcoin whitepaper, and it’s clear why.
B-money proposed a system called Proof of Work (used in Bitcoin mining) and the use of a distributed database where users could sign their transactions. The second version of b-money also describes an idea similar to staking, which is used in other cryptocurrencies today.
Ultimately, B-money never took off because the project couldn't get beyond the rough draft. However, Bitcoin clearly took its inspiration from the concepts that Dye provided.
Bit Gold
The similarities between Bit Gold and Bitcoin are so great that some believe that Nick Szabo is Satoshi Nakamoto. At its core, Bit Gold consists of a register in which rows of data obtained as a result of the Proof of Work algorithm are recorded.
Like B-money, this coin did not receive any further development. However, Bit Gold's similarities to Bitcoin have earned it the title of "Bitcoin's predecessor."
Chapter 2 - Where do new bitcoins come from?
Content
How are new coins created?
How many Bitcoins have already been mined?
How does Bitcoin mining work?
How long does it take to mine a block?
How are new coins created?
Bitcoin has a limited supply and not all units are in circulation yet. The only way to create new coins is through a process called mining - a special mechanism for adding data to the blockchain.
How many Bitcoins have already been mined?
The protocol fixes the maximum supply of Bitcoin at twenty-one million coins. As of 2020, just under 90% has been mined, but the remaining Bitcoins will take over a hundred years to produce. This is due to a periodic event called halving, the purpose of which is to gradually reduce the mining reward.
How does Bitcoin mining work?
Mining allows participants to add blocks to the blockchain. To do this, they must direct their computer's processing power to solve a specific cryptographic puzzle. As an incentive, there is a reward available to anyone who finds the appropriate solution and forms a valid block.
In order to form a block, a large amount of resources is required, while it is very simple to check its validity. If someone tries to trick the network and add an invalid block, such a request will be immediately rejected and the miner will not receive payment for mining.
The reward, often referred to as a block reward, consists of two components: transaction fees and a block subsidy. The block grant is the only source of “fresh” bitcoins. With each block mined, a unit is added to the total coin supply.
How long does it take to mine one block?
The protocol adjusts the mining difficulty so that finding a solution for a new block takes approximately ten minutes. Blocks are not always mined for exactly ten minutes; this setting is a kind of guideline for all network participants.
How to start using Bitcoin
Content
How to buy Bitcoin?
How to buy Bitcoin with a credit/debit card
How to buy Bitcoin on P2P markets
What can you buy using Bitcoin?
Where can you pay with Bitcoin?
What happens if I lose my bitcoins?
Is it possible to cancel a Bitcoin transaction?
Can I make money with Bitcoin?
How to properly store your bitcoins?
Storing Bitcoin on Binance
Storing your coins in a Bitcoin wallet
Hot wallets
Cold wallets
How to buy Bitcoin?
How to buy Bitcoin with a credit/debit card
Binance allows you to purchase Bitcoins seamlessly through your browser. To do this you need to follow these steps:
Go to the section: “Buy and sell cryptocurrency.”
Select the cryptocurrency you want to buy and the currency in which you will make the payment.
Login to Binance or register if you don't already have an account.
Select a Payment Method.
If necessary, enter your card details and confirm your identity.
That's all! Your Bitcoin will soon be credited to your Binance account.
How to buy Bitcoin on the P2P market
You can also buy and sell Bitcoin on the P2P market. This allows you to buy coins from other users directly from the Binance mobile app. To do this you will need:
Launch the application, go through the registration process if you do not have your own account and log in.
Select "One-Click Buy and Sell" and then click on the "Buy" tab in the top left corner of the interface.
You will be offered several different payment options, click "Buy" next to the one you want to use.
You can also make a payment using other cryptocurrencies (Buy crypto tab) or fiat currency (Buy fiat tab).
Below you will be asked to indicate your payment method. Choose the one that suits you best.
Select Buy BTC.
Now you must make the payment. Once the payment has been completed, click Mark as Paid and then confirm the transaction.
The transaction is completed when the seller sends you the coins.
Do you want to start using cryptocurrency? Buy Bitcoin on Binance!
What can you buy using Bitcoin?
There are many things you can buy with Bitcoin. Today, you may have some difficulty trying to find merchants who officially accept Bitcoin as a means of payment in brick-and-mortar stores. However, you can find many websites that accept the first cryptocurrency or allow you to buy gift cards with it for other types of services.
Here are just some of the things and services you can buy using Bitcoin:
Airplane tickets
Hotel room rental
Real estate
Food and drink
Cloth
Gift certificates
Online subscriptions
Where can you pay with Bitcoin?
There are so many places you can spend your Bitcoin, and more are becoming available every day! Let's look at some of them.
TravelbyBit
Save on big credit card fees on your travels around the world! You can book flights and hotels using Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies thanks to TravelbyBit. Register and book the listed services in cryptocurrency and receive a 10% discount.
He will spend
Spendabit is a search engine for products you can buy with Bitcoin. Simply search for what you would like to buy and get a list of sellers from whom you can buy it using Bitcoin.
Coinmap
Finder of all cryptocurrency merchants and ATMs in your area. If you want to spend your Bitcoin and are just looking for a suitable store for this, then this resource may be the ideal option for you.
Bitrefill
Thanks to this service, you can purchase gift certificates for several hundred different services and even top up your phone with Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. This is quite easy to do, along with the ability to transact on the Lightning Network to pay for your purchases.

Heat map of retailers that accept cryptocurrency as a means of payment. Source: https://coinmap.org/
What happens if I lose my bitcoins?
Since the bank does not interact in any way with such transactions, you are solely responsible for the safety of your savings. Some prefer to store their cryptocurrency on exchanges, while others tend to use different wallets. If you prefer to use a wallet, you should definitely write down your seed phrase so that if something happens, you will always be able to restore access to your wallet.
Is it possible to cancel a Bitcoin transaction?
Once data is added to the blockchain, it will not be easy to remove and delete it (in practice, this is almost impossible to do). This means that once you make a transaction, it cannot be reversed. You should always double, or better yet triple, check that you are sending your funds to the correct address.
For an example of how a transaction can be reversed purely theoretically, see What is a 51% attack?
Can I make money with Bitcoin?
You can either make money on Bitcoin or lose it. Basically, long-term investors buy and hold Bitcoin on the assumption that it will rise in price in the future. Others prefer to actively trade it in pairs with other cryptocurrencies to make profits in the short to medium term. Both of these strategies are quite risky, but they often turn out to be more effective than low-risk approaches.
Some investors prefer to use a hybrid strategy. They hold Bitcoin as a long-term investment while trading certain trading pairs (in a separate portfolio) for the short term. There is no right or wrong way to allocate assets in your portfolio, as each investor has a different risk appetite and financial goals.
Landing is becoming an increasingly popular form of passive income. Based on lending your coins to someone else, you can receive a certain percentage that will go into your account. Platforms like Binance Lending allow you to take advantage of this earning opportunity with Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies.
How to properly store your bitcoins?
There are many options for storing coins, each with their own strengths and weaknesses.
Storing Bitcoin on Binance
A custodial solution refers to this type of storage when the user does not personally own the coins, but entrusts it to a third party. To make transactions, you first need to log into a third party platform. Exchanges like Binance often use this model as it is much more efficient and convenient for trading.
Storing your coins on Binance allows you to easily access your trading activities or landing page.
Storing your coins in a Bitcoin wallet
Solutions that do not involve restrictions on the free movement of assets are the exact opposite of the previous type of storage, for the reason that they give the user control over their funds. For this type, you use something called a wallet. A wallet is not a place to store your coins; such options only contain cryptographic keys that unlock access to assets on the blockchain. There are two main types of wallets:
Hot wallets
A hot wallet is software on your device, in the form of a mobile or desktop application, that requires a constant internet connection in order to easily send and receive coins. An easy-to-use mobile wallet that supports multiple coins is Trust Wallet. Since hot wallets operate on the basis of a permanent Internet connection, they are more convenient to use for sending various payments, but in turn, such solutions are more vulnerable to hacker attacks.
Cold wallets
Cryptocurrency wallets that are not influenced by the Internet are called cold wallets. They are much more resistant to hacker attacks due to the lack of online attack vectors, but therefore tend to provide a less convenient user experience. An example would be hardware or paper wallets.
If you want more details on this topic, we recommend that you read our article: “Types of wallets for storing cryptocurrency.”
Chapter 4 - Bitcoin Halving
Content
What is Bitcoin halving?
How it works?
Why is this happening?
What does halving affect?
When is the next Bitcoin halving?
What is Bitcoin halving?
A Bitcoin halving (sometimes referred to as a Bitcoin halvening) is simply an event that reduces the block reward. As soon as the halving occurs, the reward that miners receive for validating new blocks is divided in two (after the halving, miners receive only half of what they received before). However, this does not affect transaction fees.
How it works?
When Bitcoin first launched, miners received 50 BTC for each block validation.
The first halving occurred on November 28, 2012. At this point, the protocol reduced the block subsidy from 50 BTC to 25 BTC. The second halving took place on July 9, 2016 (from 25 BTC to 12.5 BTC). The next one, which should take place in May 2020, will reduce the reward to 6.25 BTC.
You can trace a certain pattern. Paying attention to the dates, halving occurs every 4 years. While this is a foreseen event, the protocol does not require any specific dates to be set. Instead, the halving time is determined by the block height, so the halving occurs every 210,000 blocks. Based on this information, we can expect the subsidy to be halved after 2,100,000 minutes (remember it takes ~10 minutes to mine a block).

In this graph, we see the decrease in the block subsidy over time and its relationship with total supply. It may seem to you that the reward amount has dropped to zero, and the maximum supply is already circulating in the market, but this is not so, for the reason that the curves are located incredibly close to each other. The subsidy is expected to reach zero around 2140.
Why is this happening?
This process is one of the main features of Bitcoin that Satoshi Nakamoto never got around to explaining, as well as why he limited the total supply to twenty-one million units. Some speculate that it is nothing more than a regular financial product, starting with a block subsidy of 50 BTC, which is halved every 210,000 blocks.
Having a limited supply means that the currency will not be prone to depreciation in the long term. This is in stark contrast to fiat money, which loses its purchasing power over time as new units come into circulation.
It also makes sense to limit the speed at which participants can mine coins. One should take into account the fact that 50% was generated by the block at an altitude of 210,000 (i.e. by 2012). If the subsidy had remained at the same level, all units would have been produced by 2016.
The way halving works provides an economic stimulus for more than 100 years. This gives the Bitcoin system enough time to attract users in order to develop an internal market for transaction validation fees.
Do you want to start using cryptocurrency? Buy Bitcoin on Binance!
What does halving affect?
Those who suffer the most from the halving are the miners. This is because the block grant constitutes a significant portion of their income. When the halving occurs, miners begin to receive only half of their reward for the same amount of work. Also, their reward consists of transaction fees, but today, this amount is only a part of the block reward.
Thus, halvings can make mining unprofitable for a certain category of participants. It is not yet known how this may affect the entire industry as a whole. However, reducing block rewards could lead to further centralization of mining pools or simply encourage the development of more efficient mining implementations.
If Bitcoin continues to rely on the Proof of Work algorithm, then the cost of the commission will need to increase to maintain mining profitability. This scenario is quite possible if blocks begin to include more transactions. In case of a large number of pending transactions, transactions with a higher commission will be processed first.
Historically, a sharp increase in the value of Bitcoin is accompanied by halving. There isn't much data on this since it only happened twice. Many attribute this price movement to a shortage of bitcoins on the market and a halving of the influx of new coins. Proponents of this theory believe that after the event in May 2020, the price of the first cryptocurrency will skyrocket again.
Another part of users does not agree with this, arguing that the news about the halving has already been reflected in the market (see the details in the efficient market hypothesis). While this event comes in the form of a surprise, participants have known for over a decade that the block reward will be reduced in May 2020. It is also often mentioned that the past explosive growth is partly due to the fact that the industry was extremely underdeveloped during the first two halfings. Nowadays, the market has become much more popular, offering sophisticated trading instruments, thereby inviting a wider range of investors to participate.
When is the next Bitcoin halving?
The next halving is expected in May 2020, after which the reward for mining a block will drop to 6.25 BTC. Follow our countdown to the Bitcoin halving on Binance Academy.
Common Misconceptions About Bitcoin
Content
Is Bitcoin an anonymous currency?
Is Bitcoin a scam?
Is Bitcoin a Bubble?
Does Bitcoin use encryption?
Is Bitcoin an anonymous currency?
The short answer is no. Bitcoin may seem anonymous at first, but this is completely wrong. The Bitcoin blockchain is public, and anyone can view all transactions on the network. Your identity is not tied to your wallet addresses on the blockchain, but a third-party viewer with the necessary resources could potentially link them together. It would be more accurate to say that Bitcoin is a pseudonymous currency. Bitcoin addresses are visible to everyone, but the names of their owners are not.
However, the system is relatively private, and there are methods that can make it even more difficult for third-party viewers to determine the movements of your Bitcoins. Freely available technologies can create plausible deniability to "break the connection" between addresses. Moreover, future updates may significantly improve privacy, see "Introduction to Confidential Transactions" for an example.
Is Bitcoin a scam?
Answer: no. Just like paper money, Bitcoin can be used in illegal activities, but this does not make it a scam.
Bitcoin is a digital currency that does not have a single regulatory authority. Detractors call it a pyramid scheme, but it doesn't fit the definition to begin with. This type of digital currency functions the same way whether it costs $20 or $20,000 per coin. Bitcoin is more than ten years old and this technology has already proven its security and reliability.
Unfortunately, Bitcoin is used in many scams that you should be aware of. These may include phishing and other social engineering schemes such as fake giveaways and airdrops. Make it a rule that if it sounds too good to be true, it's probably a scam. Never give your private keys or seed phrase to anyone, and be wary of scams that offer to increase the amount of your currency with little risk on your part. If you send your coins to a scammer or a fake giveaway, you will lose them forever.
Is Bitcoin in a Bubble?
During the period of sharp parabolic increases in the price of Bitcoin, many people appeared who believed that this was a speculative bubble. Many compared Bitcoin during these periods to tulip mania or the dot-com bubble.
Due to the unique nature of Bitcoin as a digital, decentralized product, its price is entirely determined by free market speculation. Thus, there are many factors that influence the price of Bitcoin, which ultimately determine supply and demand in the market. Since the supply of Bitcoin is limited and coins are issued on a strict schedule, it is expected that in the long term, demand will exceed supply.
Also, cryptocurrency markets are relatively small compared to traditional ones. This means that Bitcoin and other crypto assets tend to be more volatile, and it is quite common to see short-term imbalances between supply and demand.
In other words, Bitcoin can be a volatile asset at times. But volatility is a part of financial markets, especially those with relatively low volume and liquidity.
Does Bitcoin use encryption?
Answer: No. This is a common misconception because the Bitcoin blockchain does not use encryption. Each peer on the network needs to be able to read transactions to ensure they are valid. Instead, digital signatures and hash functions are used. Although some digital signature algorithms use encryption, this is not the case with Bitcoin.
However, it is worth noting that many apps and cryptocurrency wallets use encryption to further protect user password wallets. Such encryption methods have nothing to do with the blockchain, they are simply integrated into the technologies that use it.
Chapter 6 - Bitcoin Scalability
Content
What is scalability?
Why is scalability necessary for Bitcoin?
How many transactions can be processed on the Bitcoin network?
What is Lightning Network?
What is a fork?
Soft fork
Hard fork
What is scalability?
Scalability is a measure of a system's ability to evolve to meet growing demand. If you're hosting a website full of requests, you can scale it up by adding more servers. If you want to run more intensive applications on your computer, you can update its components.
In the context of cryptocurrencies, we use this term to simply describe updating a blockchain network to increase the number of transactions it can process.
Why is scalability necessary for Bitcoin?
To function properly and consistently as a daily payment solution, Bitcoin must be a fast currency. In its current form, it has a relatively low throughput, which in turn means that each block can only process a limited number of transactions.
As you already know from the previous chapter, miners receive a portion of the block reward in the form of transaction fees. Users attach them to their transactions to incentivize miners to add the transaction to the blockchain.
In turn, miners strive to recoup their investments in equipment and electricity, so they prefer transactions with higher fees. If there are a large number of transactions in the network's "waiting room" (called a mempool), the fee may increase significantly as users want to make transfers faster. In the worst case, the average commission was over $50.
How many transactions can be processed on the Bitcoin network?
Based on the average number of transactions per block, Bitcoin can currently process approximately five transactions per second. This is much lower than centralized payment solutions and is one of the main costs of using a decentralized currency.
Since Bitcoin is not controlled by a data center owned by a single legal entity, the Bitcoin network must independently limit the size of its blocks. It is possible to integrate a new block size that will allow up to 10,000 transactions per second, but this may damage the decentralization of the network. Remember that full nodes should upload new information approximately every ten minutes. If it becomes too burdensome for them, they will likely go offline.
If the protocol is used for such payments, Bitcoin enthusiasts believe that efficient scaling can be achieved in various other ways.
What is Lightning Network?
The Lightning Network is a proposal to solve Bitcoin's scalability problems. We call this a layer two solution because transactions are built outside of the main blockchain. Instead of recording all transactions at the base layer, they are processed by another protocol built on top of it.
The Lightning Network allows users to send funds for free and almost instantly, with no bandwidth restrictions (as long as users are able to both send and receive currency). To use Bitcoin on the Lightning Network, two participants lock their coins in a special address. This address has a unique property: it sells bitcoins only if both parties agree.
From this address, the parties maintain a private ledger of transactions, which can redistribute balances without transmitting information about this to the main chain. They publish the transaction to the blockchain once all necessary transfers have been completed, and the protocol then updates wallet balances. Please note that all participants do not need to trust each other. If someone tries to cheat, the protocol will quickly identify and stop any fraudulent activity.
In general, such a payment channel requires the user to have two transactions in the chain, one for replenishing his address and the other for the subsequent distribution of coins. This means that channel members can make thousands of transfers during this time period. With further development and optimization of the technology, this could become a critical component for large blockchain systems.
For a more detailed description of scalability issues and their potential solutions, see the article “Blockchain Scalability – Sidechains and Payment Channels.”
What is a fork?
Since Bitcoin is open source, anyone can modify its software. You can add new rules or remove old ones to suit different needs. However, not all changes are created equal: some updates will make your node incompatible with the network, while others will be backwards compatible.
Soft fork
A soft fork is a rule change that allows updated nodes to interact with old ones. Let's take block size as an example. Let's say we have a block size of 2 MB and only half the network has decided to accept the update, after which all blocks should not exceed 1 MB. Updated nodes now reject blocks larger than the allowed size.
Old nodes can still accept such blocks or distribute their own. This means that all nodes remain part of the same network, regardless of which version they are using.
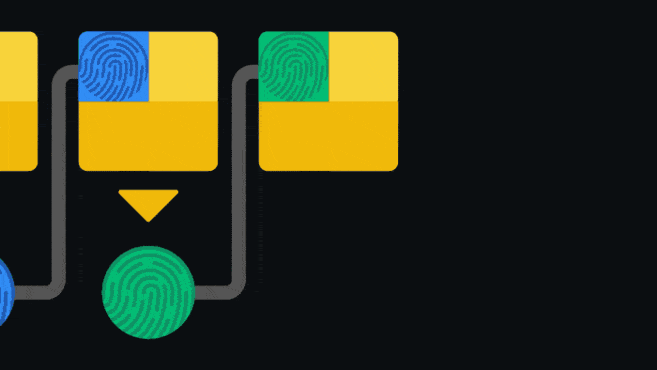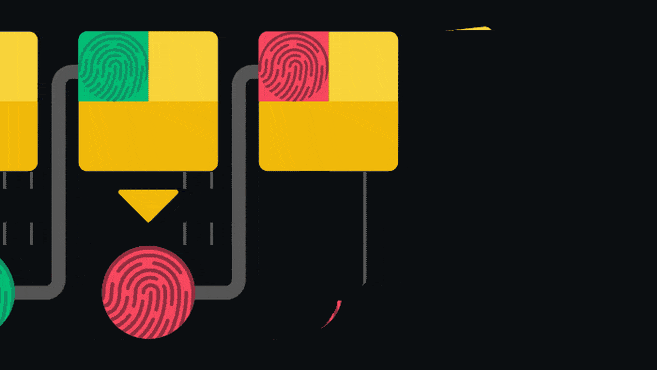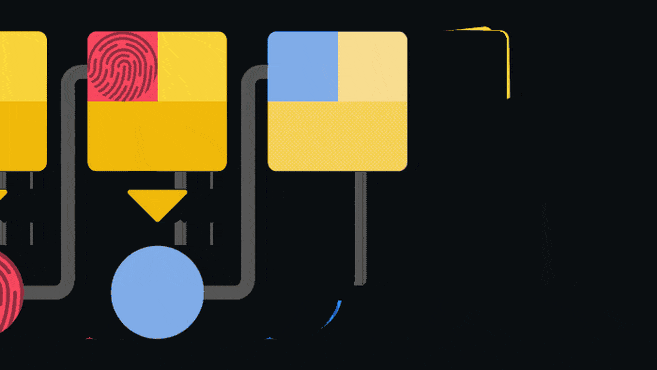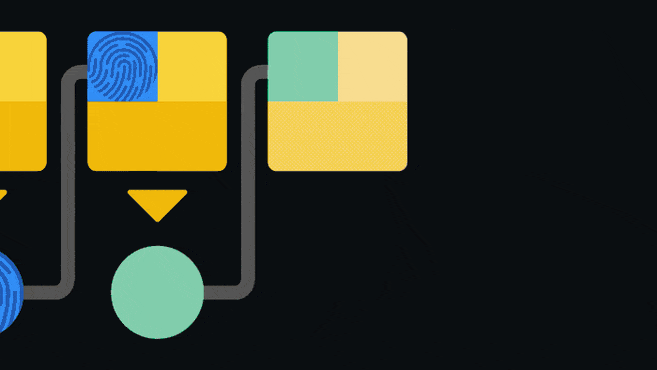
In the animation below we can see that 1 MB blocks are accepted by both old and upgraded nodes. However, newer nodes will not recognize 2MB blocks since they already follow the new rules.

The Bitcoin update called Segregated Witness (or SegWit) is one example of a soft fork. Through clever use of technology, it introduced a new format for blocks and transactions. Old nodes still continue to receive blocks, but they cannot validate the new transaction type.
Hard fork
In turn, a hard fork is more destructive. Let's say that half the network wants to increase the block size from 2 MB to 3 MB. If you try to send a 3MB block to non-updated nodes, they will reject it because the rules clearly state that the maximum size they can accept is 2MB. Since the two networks are no longer compatible, the blockchain splits into two separate networks.

The black chain in the diagram above is the original one. Block 2 is where the hard fork occurred. After the fork, the updated nodes began to produce larger blocks (green). The old nodes will not recognize them, so they will continue to take a different path. As a result of this event, two blockchains appeared, which are united by a common transaction history up to block 2.
Now there are two different protocols, each with its own currency. All information is completely duplicated in the new network, which means that if you had 20 BTC in the original chain, then you will also have 20 NewBTC in the new one.
In 2017, Bitcoin experienced a rather controversial hard fork following a similar scenario. A minority of participants wanted to increase the block size to provide higher throughput and reduce transaction fees. The rest of the network thought this was a pretty bad scaling strategy. Ultimately, the hard fork gave birth to Bitcoin Cash (BCH), which broke away from the Bitcoin network and now has its own independent community and roadmap.
To learn more about forks, see the article: “Hard forks and soft forks.”
Participation in the Bitcoin network
Content
What is a Bitcoin node?
How does a Bitcoin node work?
Full nodes
Simplified nodes
Mining nodes
How to run a full Bitcoin node
How to mine Bitcoin
How long does it take to mine Bitcoin?
Who can make changes to the Bitcoin code?
What is a Bitcoin node?
A Bitcoin node is a term used to describe a program that acts as a bridge for user equipment to interact with the Bitcoin network. This could be anything from a mobile phone from which a Bitcoin wallet is managed, to a separate computer on which a complete copy of the blockchain network records is stored.
There are several types of nodes (network nodes), each of which performs specific functions. All of them act as the end point of communication with the network, the main task of which is to transmit information about transactions and blocks in a timely manner.
How does a Bitcoin node work?
Full nodes
A full node validates (checks) transactions and blocks to ensure that certain network requirements are met (i.e. they follow the rules). Most full nodes use software called Bitcoin Core, which is the reference implementation of the Bitcoin protocol.
Bitcoin Core is a program created by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009, at the time it was simply called Bitcoin, but was later renamed to avoid confusion. You can also use other implementations of similar software, provided that they are compatible with Bitcoin Core.
Full nodes are an integral part of Bitcoin's decentralized environment. They download and validate blocks and transactions, and then distribute information about the work done to the rest of the network. Because they independently verify the authenticity of the information they are provided, the user does not rely on a third party for anything.
If a full node stores a complete copy of the blockchain network, this data source is called a full node archive. However, some users refuse to store information about old blocks to save space, due to the fact that the Bitcoin blockchain contains more than 200 GB of transaction data.

Map of the location of full Bitcoin nodes. Source: bitnodes.earn.com
Simplified nodes
Simplified nodes are not as efficient and less resource-intensive, unlike full nodes. They allow users to interact with the network, but without performing all the operations that a full node does.
While a full node downloads all blocks for verification, a simplified node downloads only part of each block (the so-called block header). Although the block header is tiny in size, it contains information that allows users to fully verify the transactions in a particular block.
Lightweight nodes are ideal for devices with bandwidth (bandwidth) limitations. Typically, this type of node is used in desktop and mobile wallets. However, they cannot perform validation, thereby making lightweight nodes dependent on the operation of full nodes.
Mining nodes
Mining nodes are full nodes that, in addition to other tasks, perform an additional task - producing blocks. As we mentioned earlier, to do this they need special hardware and software to add data to the blockchain.
Mining nodes look at pending transactions and hash them along with other information to generate a specific number. If this number falls below the target value set by the protocol, the block is valid and can be broadcast to other full nodes.
In order to mine a block without relying on someone else, miners are forced to run a full node, otherwise they will not be able to figure out which transactions to include in the block.
If a network participant wants to mine, but does not want to run a full node, he can connect to a server that will provide him with the necessary information. If you are working in a pool (i.e. working with others), only one person needs to run a full node.
For more details about the types of nodes and their purpose, see the article “What are nodes (nodes)”?
How to run a full Bitcoin node
A full node can be useful for developers, merchants and end users. Running the Bitcoin Core client on your hardware gives you privacy and security benefits, and strengthens the Bitcoin network as a whole. With a full node, you will no longer rely on anyone else to directly interact with the ecosystem.
Several Bitcoin-focused companies offer users unique “play-and-play” nodes. The pre-assembled hardware is delivered to the consumer, who only needs to turn it on to begin downloading the blockchain data. This can be much more convenient for less technically aware users, but in general these solutions are significantly more expensive than setting up your own devices.
In most cases, an old PC or laptop is enough for this. It is not recommended to run a node on your everyday computing device as it can slow it down significantly. The blockchain is constantly growing, so you need to make sure that you have enough free space on your hard drive to download all the information about the network.
A 1 TB hard drive will be sufficient for the next few years, provided there are no major changes to the block size. Other requirements include 2 GB of RAM (the default, which is generally higher on most computers) and high bandwidth.
We recommend that you read the detailed description of the process of setting up a full node on bitcoin.org.
How to mine Bitcoin
In the early days of Bitcoin, early users had the ability to create new blocks using a regular laptop. Since the system was unknown to many, not many people competed in the field of mining. Due to very low activity, the protocol was adjusted and set the mining difficulty to low.
As the network's hashrate rapidly gained momentum, participants needed to upgrade their hardware to remain competitive. By moving to different types of hardware, the mining industry eventually entered the era of application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs).
As the name suggests, such devices are created for one single purpose. They are extremely effective, but for only one task. So, ASIC mining is specialized computer hardware that is used exclusively for mining and nothing more. A Bitcoin ASIC can only mine Bitcoins, but will not be able to mine other coins that do not use a similar algorithm.
Today, Bitcoin mining requires significant investment, not only in equipment, but also in electricity. At the time of writing, a good mining device can perform up to ten trillion calculation operations per second. While ASICs are very efficient, they consume a huge amount of electricity. Unless you have access to multiple mining rigs and cheap electricity, you are unlikely to be able to make a profit mining Bitcoin.
Setting up your devices for mining is a fairly simple procedure, since many ASICs are immediately supplied with internal software. The most popular option is to channel your mining power into a mining pool, where you and other participants will try to discover and mine a block. If you manage to do this, you will receive a portion of the block reward in proportion to your hashrate.
You can also mine alone, working for yourself. In this case, the probability of mining a block will be much lower, but you will keep the entire reward for yourself if you validate it.
How long does it take to mine Bitcoin?
It's difficult to give an exact answer because there are several different variables to consider. The speed of coin mining depends on the amount of electricity and your hashrate. You also need to consider the operating and maintenance costs of mining devices.
To get an idea of the income generated by Bitcoin mining, it is recommended to use a dedicated mining calculator to estimate the associated costs.
Who can make changes to the Bitcoin code?
Bitcoin Core software is open source, so everyone can contribute to the development of the Bitcoin system. Thanks to this, you have access to new features that will be added to more than 70,000 lines of code, as well as the opportunity to propose your own innovations. You can also report bugs, translate and improve the appearance of the documentation.
Changes to the software go through a rigorous review process. All this to ensure that the program, which processes transactions worth hundreds of billions of dollars, does not have any vulnerabilities.
If you are interested in contributing to Bitcoin, be sure to check out the details on the Bitcoin Core website or Jimmy Song's blog post where he describes his experience getting involved.

