What is Black Monday?
Black Monday is a term used to describe the sudden and severe drop in the stock market on October 19, 1987. The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), which measures the performance of the US stock market, then fell more than 22%. This event was preceded by two other sharp declines in the week before.
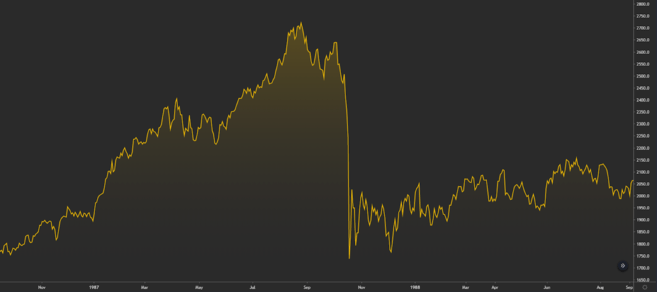
Dow Jones Industrial Average performance on Black Monday.
Black Monday is remembered as the beginning of the global decline of the stock market and today, it is one of the worst days in its history.
The overall trading volume on the exchanges was so high that the computers of that time could not cope with the sudden load on the system. Orders remained unfilled for several hours, and large money transfers were severely delayed.
Then the futures and options markets also experienced a major decline, which had a significant impact on the overall economy. By the end of the month, most major world indices lost 20-30%.
The term "Black Monday" usually refers to the crash of 1987, but it is also used to refer to other severe market declines.
What caused the market to fall?
The fall of the stock market cannot be attributed to one reason. Interestingly, the events of Black Monday 1987 were not preceded by any significant news. However, a combination of several factors provoked panic and uncertainty. So what were these factors?
The first factor was the introduction of computerized trading systems. Today, most trading transactions are facilitated by computers, but this was not always the case. Before the 1980s, stock markets were largely noisy, crowded places where traders exchanged assets directly on the exchange's trading floor.

The trading floor of the New York Stock Exchange (from the English New York Stock Exchange, abbreviated NYSE) in 1963, before the introduction of computerized trading systems. Source: Library of Congress. The original image has been modified.
In the 1980s, trading activities became heavily dependent on computer software. The move to computerized trading has allowed for much faster trading activities, with systems capable of placing thousands of orders in a matter of seconds. This also affected the speed of price movement. By comparison, modern trading bots can transfer trillions of dollars just seconds after an unexpected event.
Other factors such as the United States trade deficit, international tensions and other geopolitical circumstances have also been cited as reasons. In addition, the media played a significant role, which certainly enhanced the effect and scale of this event.
While these factors may also have contributed to the fall, it was the decisions of individuals that played a decisive role. Market psychology has a strong influence in sell-offs like these, which often occur due to mass panic.
What is a circuit breaker?
Following the events of Black Monday, the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) introduced several mechanisms to mitigate and prevent such situations and their consequences.
One of these methods is an automatic shutdown, which stops trading when the price reaches a certain percentage level relative to the day's open. Although we're primarily talking about the United States, automatic shutdown has been introduced in many other markets.
The blackout applies to major indices such as the Dow Jones Industrial Average or S&P 500, as well as individual securities. Here's how it works.
If the price of the S&P 500 declines by more than 7% during the trading day, trading stops for 15 minutes and then resumes. This is called a level 1 switch. If the market falls further and reaches 13% of the day's opening, it stops again. This is called a level 2 switch. Then, after a 15-minute break, trading resumes. If the price reaches -20% of the market open, trading stops for the rest of the day. This is called a level 3 switch.
Advantages and disadvantages of the switch
While circuit breakers can be effective in preventing flash crashes, their existence in markets has been the subject of ongoing controversy.
Some criticize this mechanism, arguing that it has a negative impact on markets and only makes the decline worse. But why does this happen? Because these percentage levels are based on market openings, they are publicly available. Thus, they can influence order placement and artificially reduce liquidity in the order book at certain price levels.
Decreased liquidity leads to greater volatility, as there simply may not be enough orders to absorb a sudden surge in supply. Critics argue that without the impact of circuit breakers on liquidity zones, markets are likely to reach a natural equilibrium.
When it comes to global stock indexes such as the S&P 500, the automatic shutdown only kicks in on big declines. On the other hand, it can be activated during sharp upward movements in the case of a separate category of securities.
How to prepare for a market crash
Due to the nature of markets and crowd psychology, falls are almost inevitable. How to prepare for a market crash?
Consider creating an investment plan or overall trading strategy. When the market falls and many investors start selling their assets in panic, it is important to remain calm, rational and avoid making emotional decisions. To do this, you need to create a long-term investment plan or trading strategy that will protect you from impulsive actions.
Another mechanism is the installation of stop loss orders. No successful trader can do without protecting short-term trades, but this method is less common among long-term investors. Even if the stop loss is set in a large price range, it can prevent huge losses when the market falls.
As for the declines in the global market, at the moment they are all temporary. Although times of economic recession can last up to several years, markets typically recover afterwards. If you look at it more broadly, the world economy is growing steadily all the time, and such corrections are only a temporary regression.
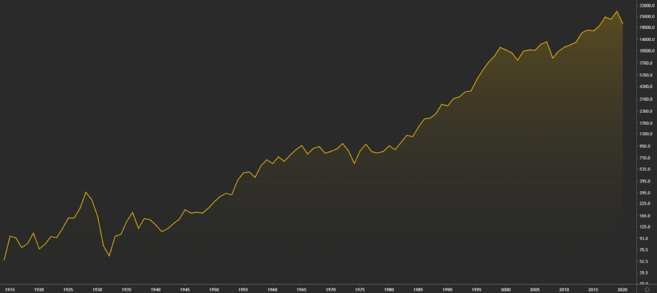
Performance of the Dow Jones Industrial Average from 1915 to 2020.
While this statement is true for global markets tied to economic growth, it does not apply to cryptocurrency markets. Because the blockchain industry is still young, cryptocurrencies are a risky asset class. Some may never recover from a severe market decline.
Are you wondering how to get started with cryptocurrencies? Buy Bitcoin on Binance!
Other famous Black Mondays
October 28, 1929
The stock market crash that preceded the Great Depression in the 1930s. Given its long-term economic consequences, the crash of fall 1929 is the most devastating stock market crash to date.
September 29, 2008
After the US housing bubble burst, stock markets began to fall. This led to the global economic crisis of the late 2000s and early 2010s. If you want to learn more about this, check out our article The 2008 Financial Crisis.
March 9, 2020
The worst day for the US stock market since the global economic crisis was caused by the coronavirus pandemic and an oil price war. At that time, it was the largest one-day drop since 2008, but this record lasted only a week, as you will learn about in the next paragraph.
March 16, 2020
Since the coronavirus outbreak, concerns about the potential economic impact of the pandemic have begun to mount. As a result, the American market experienced an even greater one-day drop than the week before. This day can be seen as the peak of the initial shock from the impact of the coronavirus on financial markets.
Summary
To summarize, Black Monday in 1987 was the major stock market crash of that time, after which the term began to be used to refer to other major stock market crashes such as in 1929, 2008 and 2020.
Subsequently, new mechanisms were introduced in an attempt to mitigate the effects of flash collapses. One of the most effective and controversial mechanisms is the circuit breaker, which stops trading when a certain percentage level of price decline is reached.
How can you prepare for a market decline? Think through possible scenarios to choose an effective investment plan or trading strategy. Study topics such as risk management, portfolio diversification, and market psychology to avoid big losses during downturns.
